|
|
SCIENCE HAPPENINGS August 2020
|
Dazzling Objects in the Night Sky
by Hannah Russell |
Billions of years ago, a star near our current solar system exploded in a brilliant supernova, throwing gases and bits of matter in many different directions. The remnants of this dramatic death left hydrogen gas and dust floating in the Milky Way galaxy along the Orion Spur of our spiral galaxy. This gas and dust began to merge, heat, and swirl together, producing a protostar. Once the temperature at the protostar’s core reached approximately 15 million Kelvin, nuclear fusion began within our sun’s center, creating a star. The leftover matter and gases from Sol’s creation began to collide, forming the rocky planets, moons, asteroids, meteoroids, gas planets, frozen bodies, and comets of our solar system approximately 4.6 billion years ago. 
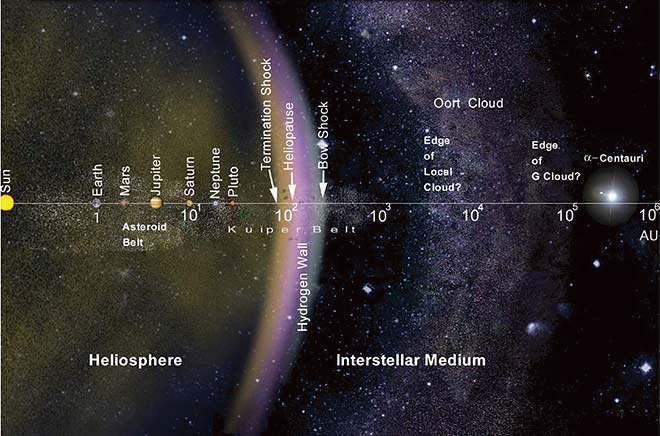
One of the most distant objects making the orbit around Sol is the icy bodies from the Kuiper Belt and the Oort Cloud. Occasionally, a comet from these regions of our solar system will pass through, allowing us to catch a glimpse like comet Neowise did last month. This comet dazzled skywatchers for most of July, resulting in beautiful photos of the tails of ionized gases and dust from the icy body as it began melting under the sun’s heat and solar winds.
The orbit of comets around the sun leaves behind bits of dust and ice along the Earth’s orbital plane. As the Earth orbits the Sol, in a predictable pattern each year, the Earth will move through these leftover bits resulting in striking meteor showers viewed here on Earth.
Annually, one of the most exciting meteor showers is the Perseids meteor shower happening this year from July 17th through August 26th. This meteor shower produces the most fireballs and has a frequency of 40-60 meteors per hour during the peak in the early am. It is a result of the passing of the comet Swift-Tuttle on its 133-year orbit. The shower’s peak will be the night between August 11th and 12th, with moonrise happening about 12:30 am. The moon will be 45% full, so getting out as soon as it is dark is advised.
|
 Southeast Utah 500 Women Scientists Mission and Values: Southeast Utah 500 Women Scientists Mission and Values:
Our Mission:
• To share the importance of science.
• To support one another as a community of women scientists in Southeast Utah
• To be in service in the name of science to the communities of Southeast Utah.
Our Values
• Being a supportive group for women scientists in Southeast Utah
• Advocate for inclusivity in our group and in science at large
• Increase scientific literacy for locals and tourists
• Mentor and support students of science (especially girls) |
|
| |
| Won’t You Be My Neighbor? - The Great Galaxy Andromedaby Spencer Stokes |
Our closest galactic neighbor has arisen in the night sky once more, the great galaxy, Andromeda. This galaxy is immense in size and it is estimated that it contains over 1 trillion stars, which is close to 10 times the size of the milky way galaxy. Even though it is the closest galaxy to our own Andromeda is roughly 3 million light years away from the earth, converted to miles it is 18 million trillion miles away. Because of its immense size and relative closeness to our own galaxy Andromeda can actually be seen with the naked eye.
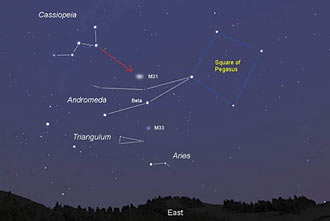
The Andromeda Galaxy was given its name because it is located in the Andromeda Constellation. The galaxy is one of the easiest deep space objects to spot due to its relative brightness and ease of direction using star hopping to find. Use this helpful guide to navigate the stars to find the wonderful Andromeda galaxy. The Andromeda constellation was named by the ancient greeks. Andromeda was a beautiful princess who’s mother bragged about her beauty. Poseidon, the god of the sea, was angered greatly by this and sent a sea monster to destroy Andromeda, who was luckily saved by the hero Peseus before Cetus, the creature, could devour her. Which is a fascinating coincidence because the Andromeda Galaxy will consume the Milky Way Galaxy in 4.5 billion years and form a much larger new galaxy. |
 |
 |
| Using binoculars or a telescope reveals a truly incredible sight. (Source, Stellarium) |
When the night is clear, try to find this amazing deep space object. Even simple binoculars will reveal some of its splendor, and remember, it is a galaxy much like our own. It is filled with millions upon billions of planets and stars. Stars that might have solar systems very similar to our own where there might be planets just like earth. (Source, NASA) |
|
| Dead Horse Point is located nine miles north of Moab on US 191, and 23 miles southwest on SR313 (32 miles total.) The visitor center is open from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. daily. Closed Thanksgiving, Christmas Day, and New Year’s Day. Park admission is $20 per vehicle and is valid for three days. |
|
|
|
|
|
© 2002-2024 Moab Happenings. All rights
reserved.
Reproduction of information contained in this site is
expressly prohibited.
|
|